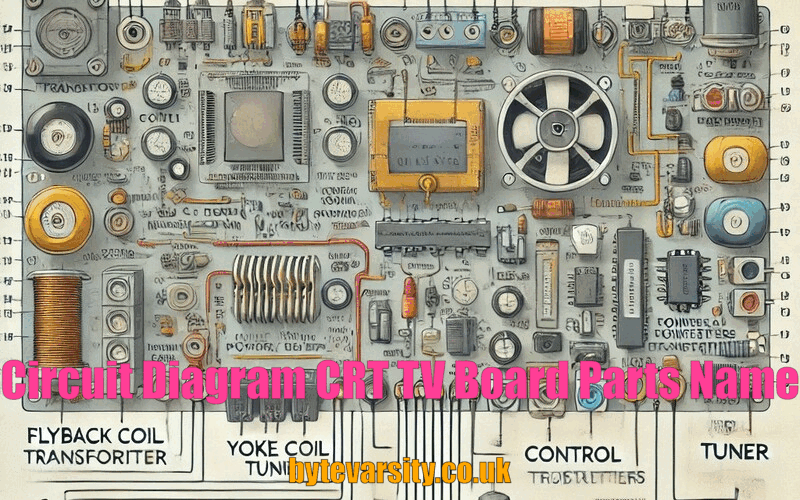
CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) TVs may seem like relics of the past, but they’ve left an impressive legacy in the world of electronics. If you’re diving into CRT TV circuit diagrams or looking to fix one up, knowing the ins and outs of its components and layout can be invaluable. Let’s jump into this guide to help you understand every part of a CRT TV board. Plus, if you’re a YouTube enthusiast looking to learn or teach about CRT repairs, this guide is perfect for creating informative videos.
Related: TV Information
Introduction to CRT TV Circuit Diagram and Board Parts
CRT TVs, known for their bulky build and unique way of displaying images, operate with complex circuitry that allows them to produce vibrant colors and sharp images. Understanding the layout of a CRT TV’s circuit board can be crucial for repairs or simply for learning how vintage electronics work. The main parts of a CRT TV board include the power supply, deflection circuits, and various capacitors and resistors.
Whether you’re new to the world of electronics or diving into CRTs as a hobby, understanding this diagram can reveal a lot about how electronics developed over the years. Let’s break down the primary parts and functions of a CRT TV circuit board.
Main Components in a CRT TV Circuit Diagram
A CRT TV circuit board has several essential parts, each playing a unique role. If you’ve ever wondered why CRTs have that distinctive “glow” or what gives them such intense color depth, it’s largely due to the unique components at work here.
Power Supply Circuit
The power supply is like the heart of a CRT TV, delivering the necessary voltage to power up each part. CRT TVs run on high-voltage circuits—sometimes as high as 25,000 volts—making this section vital for proper functioning. However, handling these components can be dangerous without the right precautions.
Many users might have noticed how CRT TVs take a moment to “warm up” before displaying an image; that’s due to the power supply ramping up and feeding energy into other circuits.
Horizontal Deflection Circuit
The horizontal deflection circuit controls the electron beam’s horizontal movement, essentially drawing lines from left to right across the screen. This circuit is integral for creating the image on the screen. Have you ever noticed that flickering effect on old CRT screens? This is typically tied to issues with the horizontal deflection circuit.
Vertical Deflection Circuit
The vertical deflection circuit is responsible for moving the electron beam up and down to complete the frame of the image. Together with the horizontal deflection circuit, it gives the screen its full, recognizable display. Problems in this circuit can lead to issues such as horizontal lines appearing on the screen or uneven image distribution.
How to Read CRT TV Circuit Diagrams
If you’re a beginner or enthusiast looking at a CRT TV schematic, it can initially look like a maze of symbols and lines. But with some guidance, you can decipher each part’s role.
Symbols and Notations in CRT Diagrams
CRT circuit diagrams are full of unique symbols representing everything from resistors to capacitors. Common symbols include the zig-zag shape for resistors and bars for capacitors. Identifying these symbols helps in locating and understanding each component’s function.
Tracing Signal Paths in CRT Circuit
Signal paths connect different components on a CRT board, forming a continuous flow of electrical current. If you can learn to trace these paths, you’ll be able to diagnose issues more effectively, seeing how one faulty part can impact the whole system.
Common Issues with CRT Circuit Boards
CRT TVs, given their age and technology, often run into specific issues that require troubleshooting. These issues range from distorted images to complete screen blackouts, typically due to worn-out components.
Capacitor Failures
Capacitors are common culprits for CRT problems. If you’ve ever seen a CRT screen flicker or noticed random color changes, it could be due to a failing capacitor. Sometimes they even show visible signs of damage, like swelling or leakage, which means it’s time for a replacement.
Horizontal and Vertical Deflection Issues
The deflection circuits are frequently at fault when image distortions happen. You may notice the image leaning to one side or experiencing flickering lines. Resolving these issues often requires checking the alignment and integrity of the deflection circuits.
Step-by-Step Guide to Repairing CRT Circuit Boards
For those who are hands-on and want to try fixing a CRT board, there are key steps to ensure safety and efficiency. But keep in mind, working on CRTs can be risky due to the high voltage, so take all necessary precautions.
Safety Precautions Before Repairing CRT TV Boards
Safety is paramount when working with CRT TVs, especially since they retain voltage even after being unplugged. Discharge the TV correctly before attempting any repairs, and wear protective gloves to avoid shock. Remember, taking shortcuts here can lead to serious injury.
Tools Required for CRT Circuit Repair
Basic tools such as screwdrivers, a soldering iron, and a multimeter are essential for CRT repairs. Each tool plays a role, whether it’s for testing connections or replacing parts. Having the right tools can make the repair process smoother and ensure each component is safely handled.
In summary, CRT TV circuit boards are complex yet fascinating, with each component—from the power supply to the deflection circuits—playing a critical role in producing the image. Understanding these parts can make troubleshooting and repairing easier. So, whether you’re repairing a nostalgic family TV or simply exploring electronics, CRT TV circuits offer a rewarding learning experience. If you’re looking for hands-on guidance, YouTube has plenty of repair tutorials that go through each part of the process step-by-step.